The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute for Space Aeronomy, the Royal Observatory of Belgium and the Royal Meteorological Institute of Belgium.
 |
Published by the STCE - this issue : 25 Jan 2013. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute for Space Aeronomy, the Royal Observatory of Belgium and the Royal Meteorological Institute of Belgium. |
| Archive of the newsletters | Subscribe to this newsletter by mail |
In the Star Trek series, the Romulan empire disposes of an advanced technology that makes their spacecraft invisible. Using this stealth technology, they sneak up behind their unsuspecting enemies, suddenly revealing themselves and blowing the enemy spacecraft to smithereens.
A Coronal Mass Ejection (CME) used its own cloaking device to wreak geomagnetic havoc last Thursday, 17 January.
On 13 January, there were several CMEs on the Sun, but they seemed either weak or not directed towards Earth. This movie (http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mrko4jH5xVk ) shows 2 CMEs between 09:00 and 15:00UT. The first CME seemed to be related to west limb activity and was directed away from Earth. The second CME was faint and slow (around 300 km/s), accompanying an impulsive M1.7-flare (peaking at 08:38UT) that originated in NOAA 1652. The plasma cloud was Earth-directed (as confirmed by STEREO - http://stereo.gsfc.nasa.gov/ ) and expected to reach Earth late on 17 January, but it seemed too faint and slow to be geo-effective. The image underneath is a combination of SOHO/LASCO C2 coronagraph (http://sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/ ) and SDO/AIA 304 (http://sdo.gsfc.nasa.gov/ ) imagery taken around 13:00UT and showing the faint CME to the north west (upper right).

It really makes you wonder what those darn CMEs are up to next!
Solar activity started at eruptive levels in the beginning of the week, but turned to quiet conditions in the second part of the week.
The 10.7 cm radio flux dropped from 154 sfu to 107 sfu.
Plenty, more then 20 C-flares were measured by GOES, most of them originating from AR NOAA 1654.
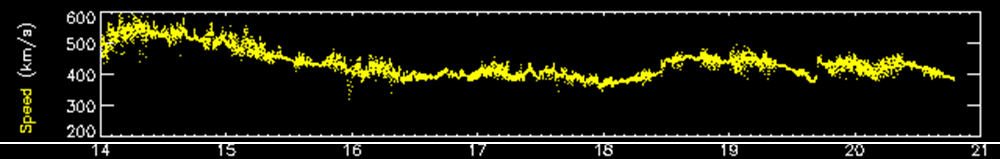
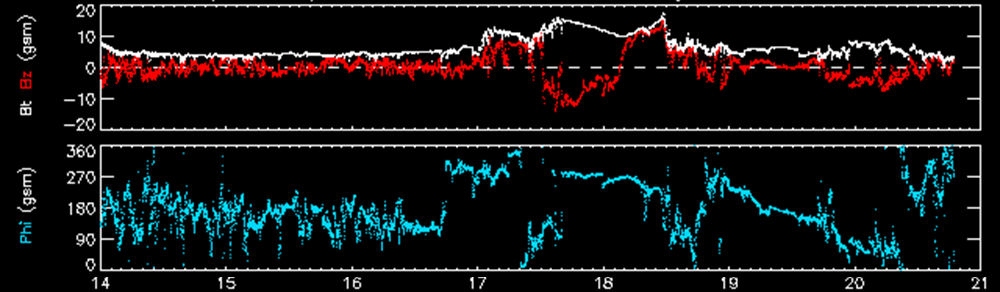
Two CME's arrived at the Earth. The first one to arrive left the Sun on Sunday Jan 13. The CME was visible in LASCO/C2 around 13:00UT. It was a faint and slow CME with a speed around 250 km/s. However, a magnetic cloud without a signature of a preceding shock did arrive on Thursday, Jan 17 around noon. The graph below shows solar wind data retrieved by the ACE spacecraft: speed, total interplanetary magnetic field, IMF and the Bz component of the IMF. The Bz component rotates from negative to positive values.
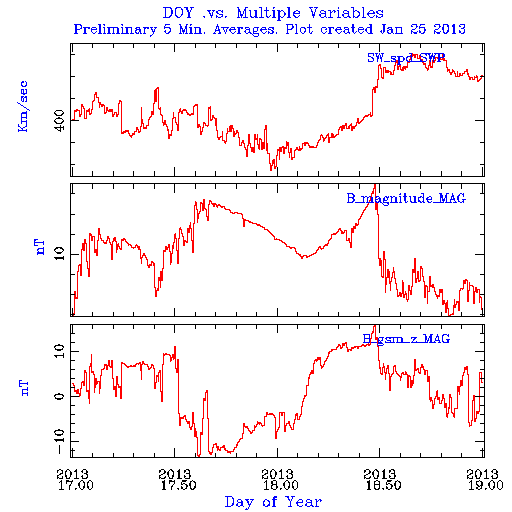
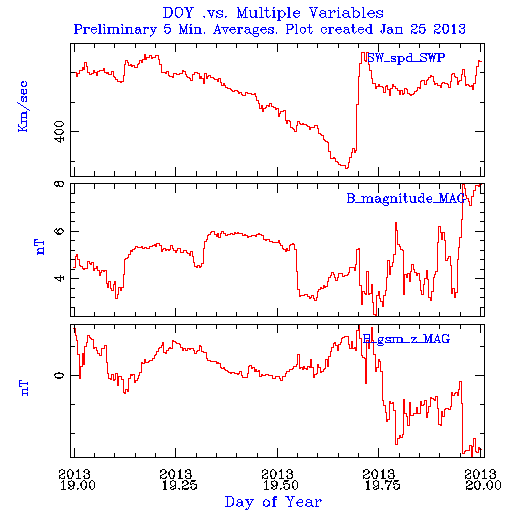
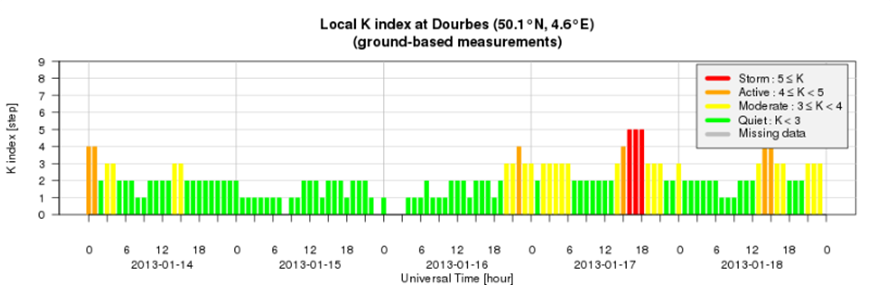
Geomagnetic conditions where generally quiet except on Thursday January 17th where Storm levels were reached in the K index and on Saturday night January 19th where Active conditions were reached, both due the CME of Sunday and Wednesday respectively.
Solar (flaring) activity was *low* during the whole week. On Wednesday it was *very low*. Back-ground EUV radiation decreased steadily during the week.
In order to view the activity of this week in more detail, we suggest to go to the following website from which all the daily (normal and difference) movies can be accessed: http://proba2.oma.be/ssa.
This page also lists the recorded flaring events.
A weekly overview movie can be found here: http://proba2.oma.be/swap/data/mpg/movies/WeeklyReportMovies/WR147/Weekly_2013_01_14_00_00_07_2013_01_20_22_54_07_SWAP_174__AIA_304-hq.mp4 (SWAP174/AIA304 combination; HelioViewer.org).
Details about some of the events in this movie can be found further below.
1. Eruption in AR11657 on Monday 14th. See here (http://proba2.oma.be/swap/data/mpg/movies/WeeklyReportMovies/WR147/Events/Eruption_SWquad_AR11657_14Jan13_030000_Diff.mp4) for a movie.
2. Prominence Eruption on Monday 15th (see also here (http://proba2.oma.be/swap/data/mpg/movies/WeeklyReportMovies/WR147/Events/Prominence_Eruption_15Jan13_070000_Diff.mp4) for a movie):
SWAP difference image
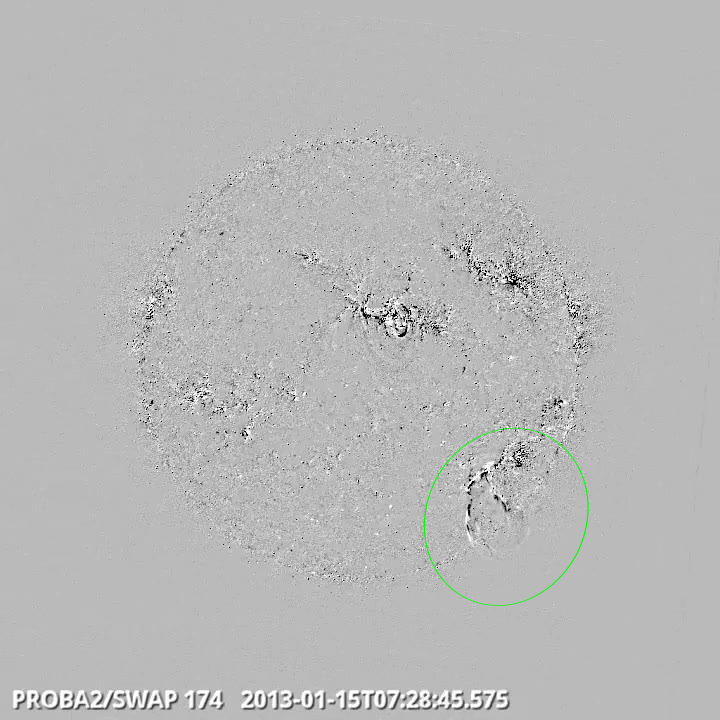
An image extracted from the SWAP movie
Start : 2013-02-04 - End : 2013-02-08
Helioseismology provides tools for imaging structures and mass
flows below the solar surface, and is becoming an essential
technique for understanding the dynamics of solar activities and
developing physics-based forecasts of the solar cycle, emerging
active regions and energy release events. A better understanding is
needed to unravel the effects of the complex interactions of solar
oscillations with the turbulent magnetized plasma
on global and local helioseismology
diagnostics. These effects are particularly challenging in regions
of strong magnetic fields. Numerical simulations of solar MHD waves
and turbulent dynamics give important insights into the complicated
wave and turbulence physics, and provide synthetic data for
verification and validation of helioseismology methods and
results.
The goals of this workshop are to discuss and stimulate further
development of helioseismology methods, solar interior models, and
realistic numerical simulations. These goals are particularly
important for analysis of the continuous data flow from the Solar
Dynamics Observatory, development and verification of
helioseismology methods, and for theoretical interpretation of
observations and inversion results.
Website:
http://sun.stanford.edu/LWS2013/
Start : 2013-02-28 - End : 2013-02-28
On February 28th, 2013 the AFFECTS team organises an
international user workshop at the Royal Observatory of Belgium in
Brussels.
At the workshop there will be a demonstration of all AFFECTS
space weather
products:
* Near real time dimming and EIT
wave detection
* 3D CME
analysis tool
* Coronal analysis tool
* CME
& solar wind
arrival and impact forecast
tool
* Flare, CME
, geomagnetic, auroral, ionospheric
forecasts & alerts
* Forecast of perturbed TEC
* Solar activity and space weather
timelines viewer
To register, please send an e-mail incl. your full name,
institution, e-mail and (institutional) address to
.
Dörte Dannemann
Website:
http://www.affects-fp7.eu/news-events/user-ws/
Start : 2013-03-04 - End : 2013-03-06
Geant4 Space Users' Workshop -G4SUW- is focused on new
results on space radiation interaction with components, sensors and
shielding analysis, as well as on Geant4-based tools and
developments applicable to space missions.
The Geant4 particle transport toolkit is jointly developed by a
world-wide collaboration and is intended for a wide range of
applications in HEP, medical field, and space physics and
engineering. In recent years, space and astrophysics has become a
significant user category, with applications ranging from
instrument and detector response verification to space radiation
shielding optimization, component effects, support of scientific
studies, and analysis of biological effects.
Main topics for next G4SUW will include:
* Single Event Effects (SEE) simulation.Geant4-TCAD
coupling.
* Microdosimetry.
* Planetary exploration applications.
* Space electronics and science detectors.
* Simulation of astronaut radiation hazards.
* Interfaces and tools to space environment analysis tools such
as SPENVIS.
* Cosmic ray magnetospheric propagation analysis.
* Large-scale simulations requiring event biasing and/or GRID
capabilities.
* General shielding optimization applications.
Website:
http://www.inta.es/g4suw2013/index.html
Start : 2013-03-26 - End : 2013-03-29
The first Solar Probe Plus Workshop will take place at the
Beckman Institute auditorium, California Institute of Technology,
Pasadena, from March 26th to 29th, 2013. SPP1 will introduce the
Heliophysics community to the mission and prepare for the exciting
discoveries that the Solar Probe Plus mission will make. The
Workshop will explore the scientific objectives of the Solar Probe
Mission and how the direct exploration of the corona and inner
heliosphere will lead to advances in our understanding of coronal
heating and solar wind acceleration, the magnetic and plasma
structure of the heliosphere, and the acceleration of energetic
particles at shocks and flares. The workshop will inspire research
that will make use of the SPP observations within the context of
the NASA Heliophysics Observatory System and identify key areas for
preparatory research. Synergistic observations from other ground
based and space based assets will also be addressed.
Website:
http://www.solarprobeplus.org/
Start : 2013-04-07 - End : 2013-04-12
The EGU General Assembly 2013 will bring together geoscientists
from all over the world into one meeting covering all disciplines
of the Earth, Planetary and Space Sciences. Especially for young
scientists, it is the aim of the EGU to provide a forum where they
can present their work and discuss their ideas with experts in all
fields of geosciences. The EGU is looking forward to cordially
welcoming you in Vienna.
Website:
http://www.egu2013.eu/home.html
Start : 2013-04-08 - End : 2013-04-12
The most recent solar minimum, solar cycle 23-24 minimum, was
unusually long (266 spotless days in 2008, the most since 1913),
and the magnetic field at the solar poles was approximately 40%
weaker than the last cycle; and unusually complex (the solar wind
was characterized by a warped
heliospheric current sheet, HCS, and fast-wind
streams at low latitudes: the
fast-wind
threads the ecliptic
more commonly in 2008 than 1996.)
This complexity resulted in many effects observed from Sun to
Earth, with many observations indicating unusual conditions on the
Sun, in the heliosphere
, and in the magnetosphere
, ionosphere
, and upper atmosphere of the
Earth.
This remarkable set of conditions provide the scientific
community with an exceptional opportunity to assess the nature and
structure of a very quiet Sun, and an upper atmosphere relatively
devoid of solar influences, helping to provide a better
understanding of the relative roles of solar activity and internal
variability in the dynamics of the Earth's upper atmosphere and
ionosphere
. Such an understanding requires a
multidisciplinary approach.
The main goal of the conference is to bring together the solar,
heliospheric, magnetospheric, upper atmosphere, and ionospheric
communities to debate and discuss interdisciplinary work and reach
a better understanding of the nature and structure of a very quiet
Sun, and of an upper atmosphere relatively devoid of solar
influences, and in doing so, to help clarify the role of solar
activity in the dynamics and variability of the Earth's upper
atmosphere and ionosphere
relative to the internal
variations.
Website:
http://chapman.agu.org/solarminimum/
Start : 2013-04-12 - End : 2013-04-12
Solar flares are impulsive releases of energy in the Sun's
corona and yet it is emission from the lower atmosphere (the
photosphere and chromosphere) that contains the bulk of the energy.
This radiation also provides some of the best diagnostics of the
flaring process. The availability of optical, UV/EUV and hard X-ray
observations, made with the current fleet of space-based (SDO,
Hinode, RHESSI, etc.) and ground-based (ROSA, IBIS, Big Bear, etc.)
observatories, combined with recent developments in flare
modelling, presents a timely opportunity to study the cause and
effect of energy deposition in the lower solar atmosphere. The
combination of multi-wavelength observations with advanced
numerical simulations can provide key insights into the processes
of particle acceleration, plasma heating, energy transport, and
wave propagation.
This Royal Astronomical Society discussion meeting will focus on
work investigating the response of the solar and stellar
atmospheres during a flare's impulsive phase and we welcome
contributions from both observation and theory.
Website:
http://www.astro.gla.ac.uk/?page_id=827
Start : 2013-04-22 - End : 2013-04-24
The workshop is being held to discuss and gather community input
on science requirements, capabilities and instrumentation for a
next-generation synoptic network of solar observing instruments. It
is highly probable that such a network should obtain
multi-wavelength data, and the intended targets include space
weather, helioseismology and solar magnetic fields.
Website:
https://www2.hao.ucar.edu/synoptic-network-workshop
Start : 2013-05-06 - End : 2013-05-10
In the last 50 years, helioseismology has made significant
contributions to the knowledge of the Sun's interior physics
and has led the way to asteroseismology. We have now reached an era
where more sophisticated questions are being asked to understand
the subtle properties of the Sun and other stars due to the
synoptic and high-resolution observations available from BISON,
GONG and space missions such as SOHO
, SDO, CoRot and Kepler.
On this occasion, a workshop on the theme of '50 years of the
seismology of the Sun and stars' is being organized to reflect the
progress that has been made as well as to focus on future goals. We
plan to bring together helio- and asteroseismologists, theorists
and observers in a journey that will take us from the interior of
the Sun and its magnetism towards the structure of distant stars
and activity cycles.
Website:
http://www.nso.edu/workshops/2013
Start : 2013-06-11 - End : 2013-06-15
Space Climate is an interdisciplinary science that deals with
the long-term change in the Sun, and its effects in the heliosphere
and in the near-Earth environment, including the atmosphere and
climate. A special focus will be on studies of the causes,
consequences and implications of the present, unusually low solar
activity since solar cycle 23 that, most likely, indicates the
imminent end of the Modern Grand Maximum of solar activity. Other
topics include solar dynamo, solar irradiance variations, solar
wind, geomagnetic field and activity, cosmic rays and cosmogenic
isotopes, and solar effects on different layers of the atmosphere
and on local and global climate, as well as possible solar effects
on human health and on the development of human cultures.
Website:
http://www.spaceclimate.fi/
Start : 2013-06-17 - End : 2013-06-20
The workshop is to improve the scientific understanding of the
origin and propagation of solar transients, and develop the
prediction capacity of these transients' arrival and potential
impact on the Earth.
This workshop is the activity of the ISEST program in CAWSES-II
/ Task Group 3. The workshop engages coordinated international
activities in observation, theory and modeling, and involves
scientists in both developed and developing countries, and provides
an online platform for educational opportunities for students.
Website:
http://spaceweather.gmu.edu/meetings/ISEST/Home.html
Start : 2013-06-23 - End : 2013-06-29
The 2013 ILWS Science Workshop will take place June 23-29, 2013
in Irkutsk, Russia and will be hosted by the Institute of
Solar-Terrestrial Physics of the Russian Academy of Sciences
Website:
http://en.iszf.irk.ru/ILWS_2013
Start : 2013-06-24 - End : 2013-06-28
Asia Oceania Geosciences Society (AOGS) was established in 2003
to promote geosciences and its application for the benefit of
humanity, specifically in Asia and Oceania and with an overarching
approach to global issues.
Asia- Oceania region is particularly vulnerable to natural
hazards, accounting for almost 80% human lives lost globally. AOGS
is deeply involved in addressing hazard related issues through
improving our understanding of the genesis of hazards through
scientific, social and technical approaches.
AOGS holds annual conventions providing a unique opportunity of
exchanging scientific knowledge and discussion to address important
geo-scientific issues among academia, research institution and
public.
Recognizing the need of global collaboration, AOGS has developed
good co-operation with other international geo-science societies
and unions such as the European Geosciences Union (EGU), American
Geophysical Union (AGU), International Union of Geodesy and
Geophysics (IUGG), Japan Geo-science Union (JpGU), and Science
Council of Asia (SCA).
Website:
http://www.asiaoceania.org/aogs2013/public.asp?page=home.htm
Start : 2013-07-12 - End : 2013-07-19
Applications are invited for the 2013 Heliophysics Summer
School, which will be held in beautiful Boulder, Colorado. We are
seeking students and undergraduate level teachers and instructors
to join us this coming summer for a unique professional experience.
Students and teachers will learn about the exciting science of
heliophysics as a broad, coherent discipline that reaches in space
from the Earth's troposphere to the depths of the Sun, and in
time from the formation of the solar system to the distant future.
At the same time, a goal of the Summer School is for the group of
instructors to develop materials from Heliophysics that can be
applied in their classes.
The Heliophysics Summer School focuses on the physics of space
weather events that start at the Sun and influence atmospheres,
ionospheres and magnetospheres throughout the solar system. The
solar system offers a wide variety of conditions under which the
interaction of bodies with a plasma environment can be studied:
there are planets with and without large-scale magnetic fields and
associated magnetospheres; planetary atmospheres display a variety
of thicknesses and compositions; satellites of the giant planets
reveal how interactions occur with subsonic and sub-Alfvenic flows
whereas the solar wind interacts with supersonic and super-Alfvenic
impacts.
Encompassed under a general title of comparative magnetospheres
are processes occurring on a range of scales from the solar wind
interacting with comets to the interstellar medium interacting with
the heliosphere. The school will address not only the physics of
all these various environments but will also go into the
technologies by which these various environments are being
observed. The program is complemented with considerations of the
societal impacts of space weather that affects satellites near
Earth and elsewhere in the solar system.
The school will be based on lectures, laboratories, and
recitations from world experts, and will draw material from the
three textbooks Heliophysics I-III, published by Cambridge
University Press.
Several teachers along with about 35 students will be selected
through a competitive process organized by the UCAR Visiting
Scientist Programs. The school lasts for eight days, and each
participant receives full travel support for airline tickets,
lodging and per diem costs.
Website:
http://www.vsp.ucar.edu/Heliophysics/
Start : 2013-07-16 - End : 2013-07-25
The Summer School Alpbach enjoys 36 years of tradition in
providing in-depth teaching on different topics of space science
& technology, featuring lectures and concentrated working
sessions on mission studies in self-organised working groups. 60
young highly qualified European science and engineering students
converge annually for stimulating 10 days of work in the Austrian
Alps. 4 teams compete to design a space mission judged by a jury of
experts. Students learn how to approach the design of a satellite
mission and explore new and startling ideas supported by experts.
The Summer School 2013 will focus on Space Weather
.
The purpose of the Summer School is to foster the practical
application of knowledge derived from lectures, to develop
organisational and team-work skills and to encourage creativity.
Teams will compete to design the best project, judged by an
independent jury. The teams themselves are responsible for the
selection of the subject of the project and for the team structure
and working methods.
Website:
http://www.summerschoolalpbach.at/
Start : 2013-09-09 - End : 2013-09-14
We gain information about the universe through analysis of the
spectra from celestial objects. However, while the intensity
spectrum represents a scalar quantity but electromagnetic radiation
occurs in the form of transverse waves, the polarized spectrum
provides us with a 4-vector, the Stokes vector. The increased
amount of information space opens new windows to the universe, in
particular for the exploration of magnetic fields. It is well
recognized that the magnetic field is a primary agent responsible
for structuring and the source of all variability on intermediate
time scales, which manifests itself in all forms of solar and
stellar activity.
It is therefore not surprising that every year there are many
scientific meetings organized with the objective of studying the
role of magnetic fields in cosmic objects. What is largely missing
in these meetings is however an in-depth investigation of the
fundamental aspects of how magnetic fields can be determined by the
means of spectro-polarimetry, our main gateway to cosmic magnetism.
The primary aim of our series of Workshops is to address these
fundamental aspects, with less emphasis on the morphological and
physical properties of cosmic magnetic fields.
Website: http://spw7.ynao.ac.cn/
Start : 2013-11-18 - End : 2013-11-22
This International CAWSES-II Symposium hosted by SCOSTEP
(Scientific Committee on Solar-Terrestrial Physics) will provide an
excellent opportunity to discuss the scientific accomplishments of
CAWSES-II and look forward to SCOSTEP's future programs at a moment
toward the end of its five-year period. The symposium will cover
the six major themes of CAWSES-II tasks: 1) What are the solar
influences on the Earth's climate?, 2) How will geospace respond to
an altered climate?, 3) How does short-term solar variability
affect the geospace environment?, 4) What is the geospace response
to variable inputs from the lower atmosphere?, 5) Capacity
Building, 6) Informatics and eScience. The main functions of
CAWSES-II are to help coordinate international activities in
observations, modeling, and applications crucial to achieving this
understanding, to involve scientists in both developed and
developing countries, and to provide educational opportunities for
students of all levels. The symposium offers keynotes/lectures that
will be interesting for all participants every morning and more
specific sessions of presentations in the afternoon. We welcome all
those who are involved and/or interested in CAWSES-II to Nagoya in
the autumn when we will have the pleasure of being surrounded by
beautiful colorful leaves of this season.
Website:
http://www.cawses.org/CAWSES/leaflet_CAWSES-II_120229.pdf
Start : 2013-11-18 - End : 2013-11-22
The 10th Edition of the European Space Weather
Week will take place on 18-22nd
November 2013 in Belgium. The venue will be confirmed early next
year, but mark your calendars now for the 10th Anniversary of this
growing European event.
The ESWW will again adopt the central aim of bringing together
the diverse groups in Europe working on different aspects of Space
Weather
. This includes but isn't
limited to the scientific community, the engineering community,
applications developers, service providers and service end users.
The meeting organisation will again be coordinated by the Belgian
Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE), ESA
and the Space Weather
Working Team. The local
organisation will be done by the STCE.
Website: not yet available
Start : 2014-08-02 - End : 2014-08-10
The 40th COSPAR Scientific Assembly will be held in Moscow,
Russia from 2 - 10 August 2014. This Assembly is open to all bona
fide scientists.
Website:
http://www.cospar-assembly.org/
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=408
A presentation given during the open doors of the public observatory Urania, Hove. 60 people participated and were instructed about our Sun, Space Weather and how PROBA2 operates as a satellite monitoring space weather. The latest scientific outcome of SWAP and LYRA, two scientific space weather instruments onboard of PROBA2 was presented.
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=409
ESWW9 Splinter wrap up of the Space Weather Working Team.
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=410
Splinter wrap up of the SWWT Topical Working Group 'Education, Outreach and Emerging Markets Topical Working Group.
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=412
Splinter wrap up of the PROBA2/SWAP and LYRA Science Meeting
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=413
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=414
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=415
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=416
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=417
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=418
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=407
ESWW9 Splinter wrap up of the SWWT topical group 'Atmospheric Effects'.
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=411