The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute for Space Aeronomy, the Royal Observatory of Belgium and the Royal Meteorological Institute of Belgium.
 |
Published by the STCE - this issue : 2 May 2013. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute for Space Aeronomy, the Royal Observatory of Belgium and the Royal Meteorological Institute of Belgium. |
| Archive of the newsletters | Subscribe to this newsletter by mail |
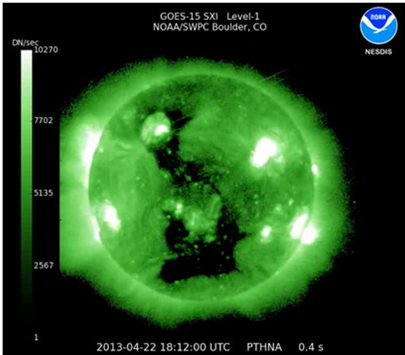
During the last fortnight, two coronal holes (one on each solar hemisphere) transited the solar disk, as shown in this clip (http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fvlckOLRbZc ) from GOES15/SXI imagery. Passing the disk's centre around 22-23 April, the high speed gusts of energetic particles created active geomagnetic conditions on 25 April and even a brief minor storm period on 26 April.
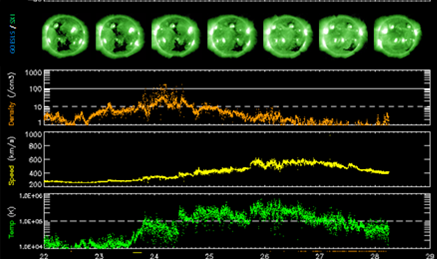
One can see the geomagnetic effects of the coronal holes (CHs) in the ACE-data underneath (http://www.swpc.noaa.gov/ace/ ), topped by a daily GOES15/SXI image. These effects were felt only about 2 days after the CHs passed the central meridian. Indeed, first some denser (orange curve), slow moving material of the solar wind passed the Earth as it was being swept up by the fast stream of the CHs (24 April). The solar wind speed then continued to gradually increase (yellow curve), and was also becoming less dense and "hotter" (more energetic; green curve), marking the true influence of the CHs.
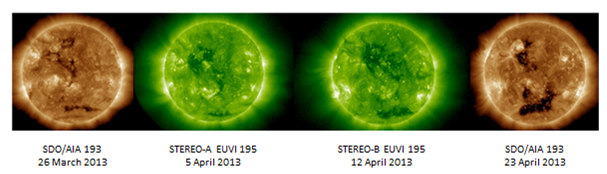
The CHs are recurrent ones, meaning they were also visible during the previous solar rotation. At that time, they were not so distinct but the northern CH still produced minor geomagnetic storm conditions lasting for several days late March. See the comments in this STCE Newsletter at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/pdf/2013/STCEnews20130404.pdf The evolution of the CHs can be seen in this clip of the synoptic maps (whole Sun) created from SDO and STEREO-A and -B imagery as the CHs transited the Sun's backside (see http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fvlckOLRbZc ).
Coronal holes usually cause only active geomagnetic conditions, with sometimes some minor storming. Based on geomagnetic data till mid-April from the Kyoto World Data Centre for Geomagnetism, there have been only 80 days with at least one 3-hours geomagnetic storming period so far this solar cycle. 31 of those were due to the influence of coronal holes (based on SWPC and SIDC reports), and the very large majority was minor storm only. Only on 2 days (2 May 2010 and 28 May 2011) there was a moderate geomagnetic storm due to a coronal hole.
Credit - Data and imagery were taken from GOES15/SXI imagery (http://www.swpc.noaa.gov/sxi/), ACE (http://www.swpc.noaa.gov/ace/), SDO (http://sdo.gsfc.nasa.gov/data/ ), STEREO-A and -B (http://stereo.gsfc.nasa.gov/), and the Kyoto World Data Centre for Geomagnetism (http://wdc.kugi.kyoto-u.ac.jp/).
On April 25, the Space Pole was flooded with kids and teenagers. That day, their self-made experiment was hooked on a weather balloon and took off to the border of space.
The balloon-experiment is an all-inclusive project. To start, the students have to excogitate an idea. What do they want to measure, what is possible to measure? They have to figure out the technical details, test if the experiment functions and survives the extreme conditions - there are some differences between the space and earth environment. When the experiment returns home, they need to analyse the results and make conclusions. This is not so straight forward as it seems.
There is something for everyone: the smallest kids send seeds or eggs from the stick insect to space, the teenagers venture space physics: what about pressure, temperature, cosmic radiation?
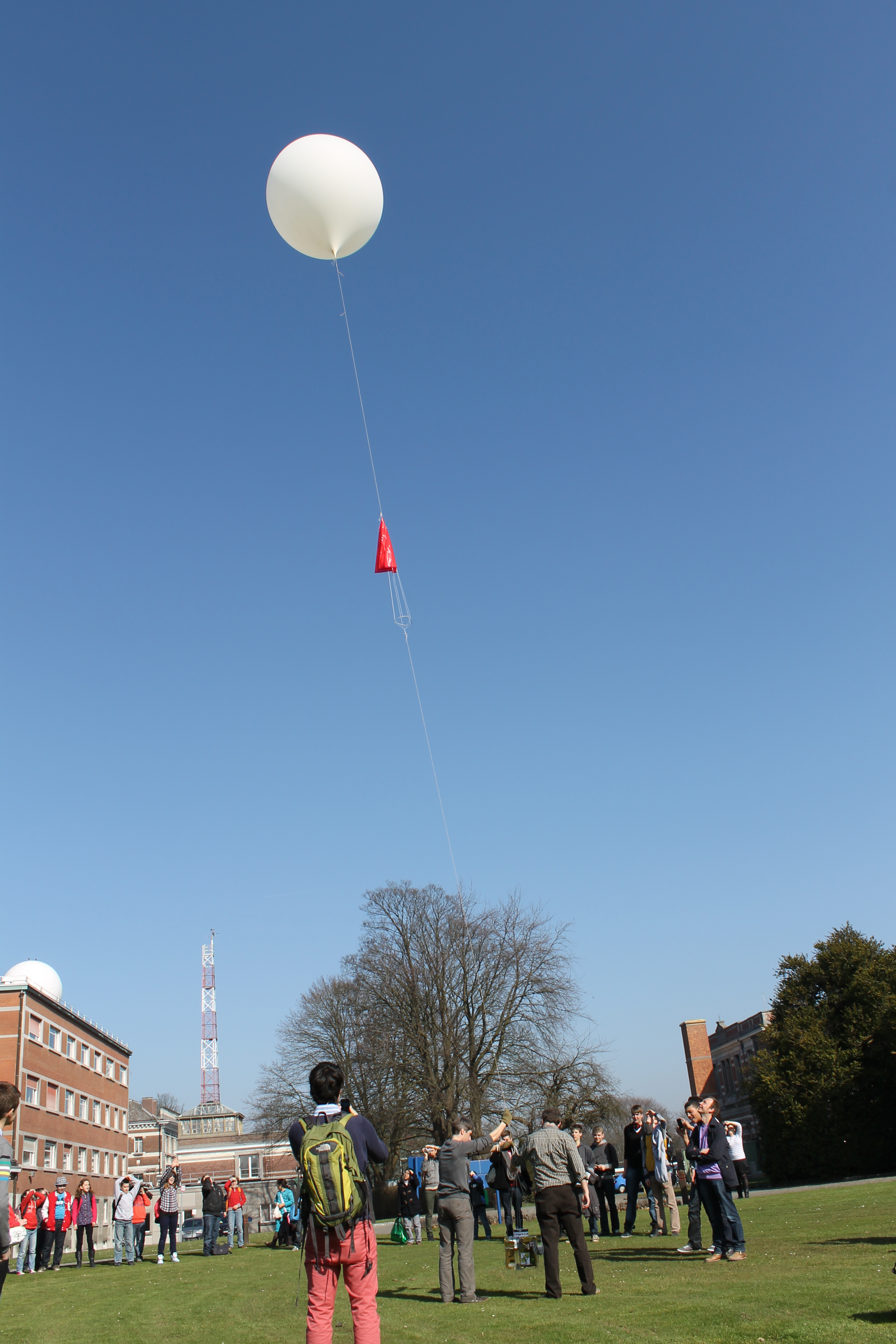

Roeland Van Malderen, one of the key persons of the project: 'The balloon experiment shows how science works: it starts with an idea and after a long process you get the measurements and your results which need to be interpreted. Maybe, one of those students chooses for a carrier as an astronomer, space expert or a carrier in meteorology and becomes a colleague.'
The common factor is that they all work towards that particular exciting moment: the launch of the balloon with their experiment onboard. One of the youngsters stated: 'When the balloon left for open air, it was - how should I say it - thrilling! Our ideas were really flying.'
At the same time, it is an adventure - you don't know if your experiment will be successful: the balloon can disappear, de gondola can crash, is your experiment really space-proof?
Anne-Lize Kochuyt, from the planetarium, is clear: 'The most important is that these kids experience science besides learning a theory from a book.'
http://www.asgard-balloons.webs.com
Solar Flaring activity was dominated by NOAA AR 1726 (Cat 51, beta-gamma-delta) which produced a large number of C-class flares. The biggest event of the period was however only a short-duration M1.0 flare on April 22.
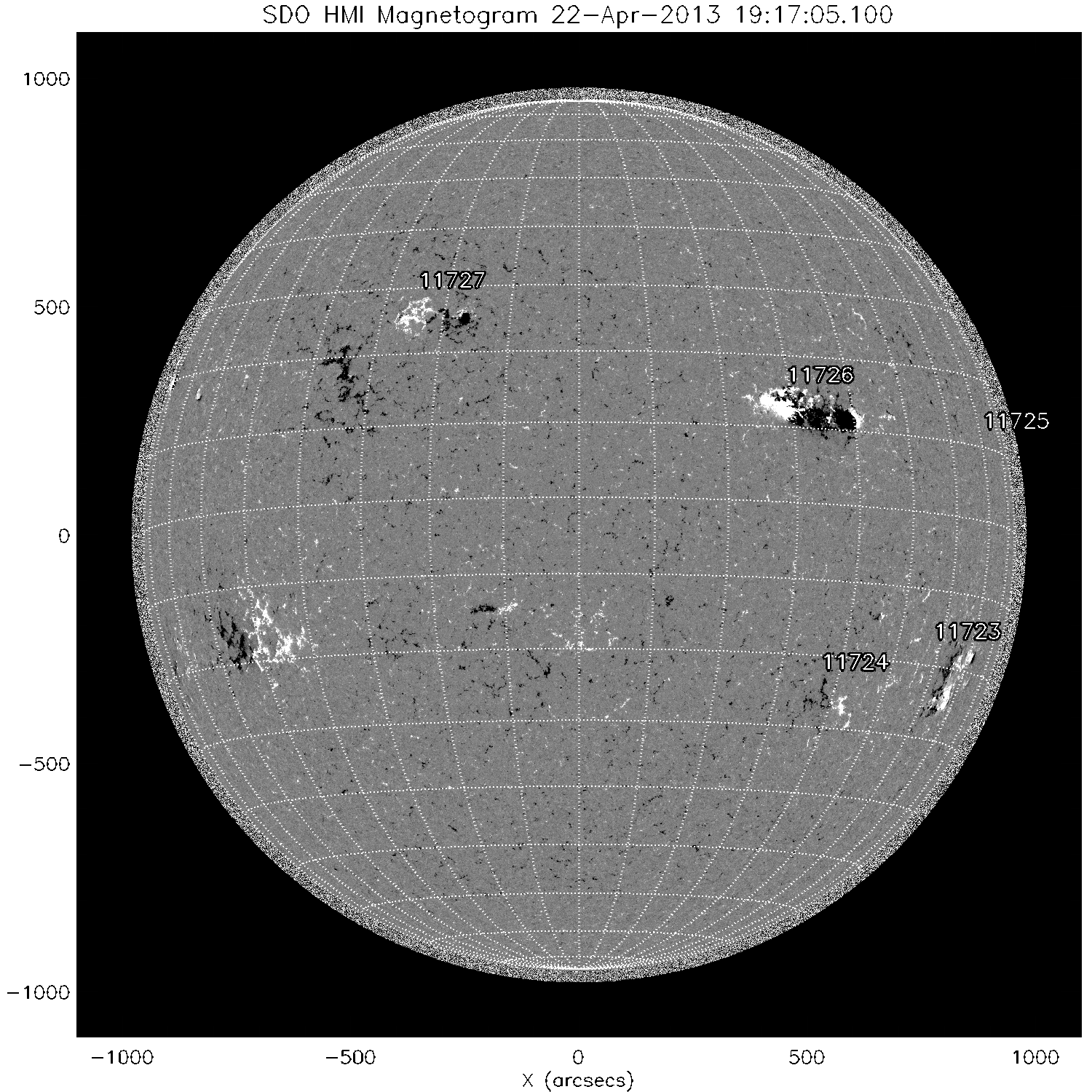

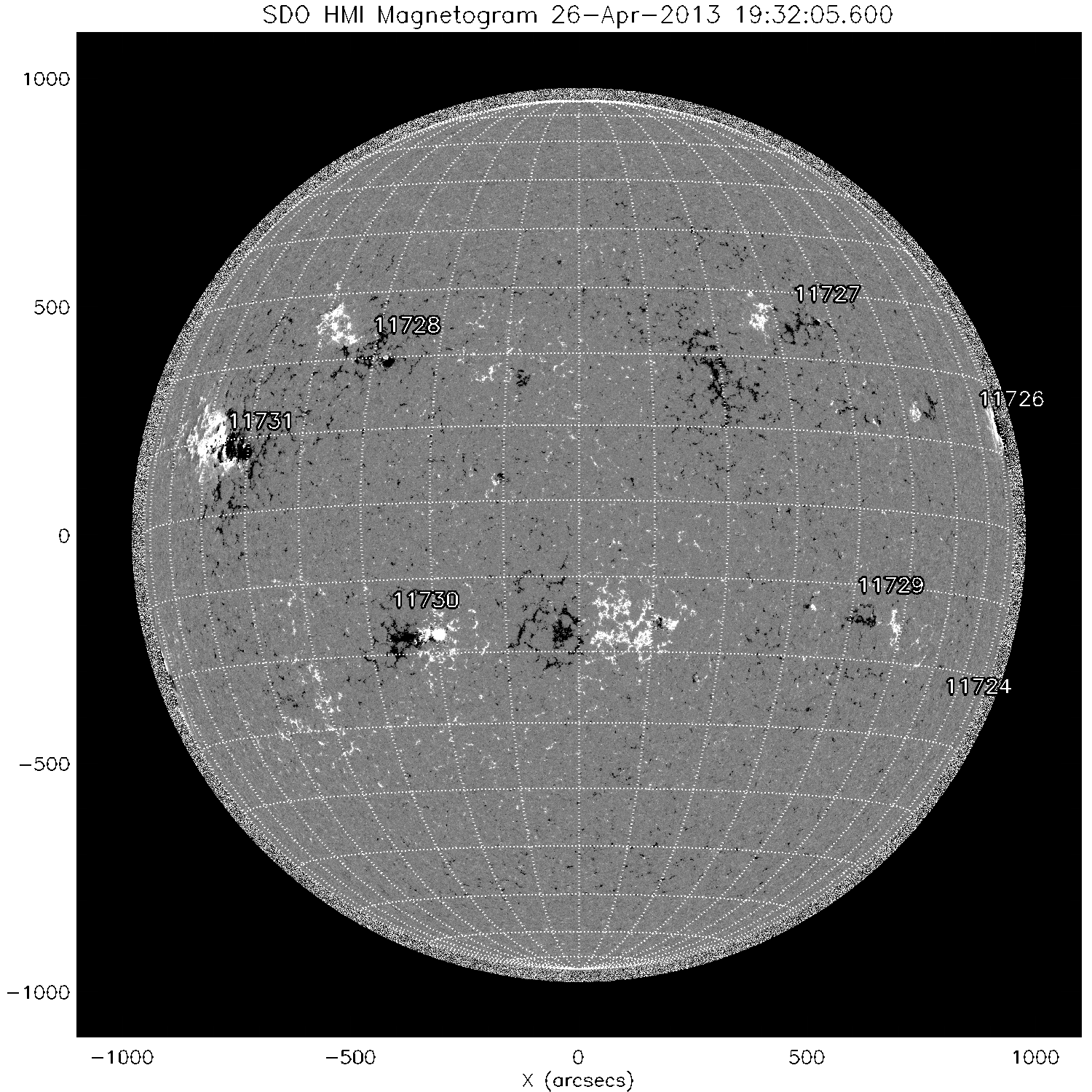
A recurrent coronal hole in the Southern hemisphere drove the geomagnetic activity during the period. The solar wind speed, as measured by the ACE satelleite, was 250 km/s in the beginning of the period and rose monotonically up till 550 km/s on late April 25 till April 27.
Towards the end of the period, the solar wind speed decreased again to 400 km/s. The associated co-rotating interactive region pushed up the solar wind density and IMF on April 24 and April 25. Local K-index (Chambon La Foret) and NOAAs estimated Kp index reached values 4. Check the news item http://www.stce.be/news/191/welcome.html
Several halo CME alerts were issued by CACTus during the period but none of these was Earth-directed.
| DAY | BEGIN | MAX | END | LOC | XRAY | OP | 10CM | TYPE | Cat | NOAA | NOTE |
| 22 | 1022 | 1029 | 1031 | M1.0 | 0 | III/3 V/3 | 1726 |
| LOC: approximate heliographic location | TYPE: radio burst type |
| XRAY: X-ray flare class | Cat: Catania sunspot group number |
| OP: optical flare class | NOAA: NOAA active region number |
| 10CM: peak 10 cm radio flux |

The figure shows the time evolution of the Vertical Total Electron Content (VTEC) (in red) during the last week at three locations:
a) in the northern part of Europe(N61°, 5°E)
b) above Brussels(N50.5°, 4.5°E)
c) in the southern part of Europe(N36°, 5°E)
This figure also shows (in grey) the normal ionospheric behaviour expected based on the median VTEC from the 15 previous days.
The VTEC is expressed in TECu (with TECu=10^16 electrons per square meter) and is directly related to the signal propagation delay due to the ionosphere (in figure: delay on GPS L1 frequency).
The Sun's radiation ionizes the Earth's upper atmosphere, the ionosphere, located from about 60km to 1000km above the Earth's surface.The ionization process in the ionosphere produces ions and free electrons. These electrons perturb the propagation of the GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) signals by inducing a so-called ionospheric delay.
See http://stce.be/newsletter/GNSS_final.pdf for some more explanations ; for detailed information, see http://gnss.be/ionosphere_tutorial.php
Presentatie over de 24ste zonnecyclus voor leden van de VVS-afdeling ASH Polaris te Herentals in het kader van hun maandelijkse voordrachten. Een basiskennis is vereist. Behandelde onderwerpen zijn zonnevlekken, de zonnedynamo, zonneuitbarstingen, ruimteweer, voorspellingen voor SC24, evolutie van SC24, verwachtingen voor het verdere verloop van SC24.
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=429
Poster for the session 4: DATA ASSIMILATION, VISUALIZATION AND ANALYSIS
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=430
Presentation given at the first annual meeting of CHARM, an Interuniversity Attraction Poles project lead by the KULeuven. The presentation introduces the university of Gent and its link with CHARM.
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=431
Presentation given at the first annual meeting of CHARM, an Interuniversity Attraction Poles project lead by the KULeuven.
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=432
Presentation given at the first annual meeting of CHARM, an Interuniversity Attraction Poles project lead by the KULeuven. The presentation introduces the solar wind group at BIRA-IASB and its link with CHARM.
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=433
Presentation given at the first annual meeting of CHARM, an Interuniversity Attraction Poles project lead by the KULeuven. The presentation introduces the Institute for Computational Cosmology at the university of Durham and its link with CHARM.
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=434
Presentation given at the first annual meeting of CHARM, an Interuniversity Attraction Poles project lead by the KULeuven.
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=435
Tutorial given at the first annual meeting of CHARM, an Interuniversity Attraction Poles project lead by the KULeuven.
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=436
Presentation given at the first annual meeting of CHARM, an Interuniversity Attraction Poles project lead by the KULeuven. The presentation introduces the university of Leiden and its link with CHARM.
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=437
Presentation given at the first annual meeting of CHARM, an Interuniversity Attraction Poles project lead by the KULeuven.
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=438
Presentation given at the first annual meeting of CHARM, an Interuniversity Attraction Poles project lead by the KULeuven.
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=439
Tutorial given at the first annual meeting of CHARM, an Interuniversity Attraction Poles project lead by the KULeuven.
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=440
Presentation given at the first annual meeting of CHARM, an Interuniversity Attraction Poles project lead by the KULeuven. The presentation introduces the Université Libre de Bruxelles and its link with CHARM.
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=441
Presentation given at the first annual meeting of CHARM, an Interuniversity Attraction Poles project lead by the KULeuven.
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=442
Tutorial given at the first annual meeting of CHARM, an Interuniversity Attraction Poles project lead by the KULeuven.
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=443
Presentation given at the first annual meeting of CHARM, an Interuniversity Attraction Poles project lead by the KULeuven.
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=444
Presentation given at the first annual meeting of CHARM, an Interuniversity Attraction Poles project lead by the KULeuven.
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=445
Presentation given at the first annual meeting of CHARM, an Interuniversity Attraction Poles project lead by the KULeuven.
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=446
Presentation given at the first annual meeting of CHARM, an Interuniversity Attraction Poles project lead by the KULeuven.
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=447
Presentation given at the first annual meeting of CHARM, an Interuniversity Attraction Poles project lead by the KULeuven. The presentation introduces the solar wind unit of BIRA-IASB and its link with CHARM.
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=448
Presentation given at the first annual meeting of CHARM, an Interuniversity Attraction Poles project lead by the KULeuven.
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=449
Presentation given at the first annual meeting of CHARM, an Interuniversity Attraction Poles project lead by the KULeuven.
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=450
Presentation given at the first annual meeting of CHARM, an Interuniversity Attraction Poles project lead by the KULeuven.
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=451
Presentation given at the first annual meeting of CHARM, an Interuniversity Attraction Poles project lead by the KULeuven.
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=452
Presentation given at the first annual meeting of CHARM, an Interuniversity Attraction Poles project lead by the KULeuven.
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=453
Presentation given at the first annual meeting of CHARM, an Interuniversity Attraction Poles project lead by the KULeuven.
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=454
Presentation given at the first annual meeting of CHARM, an Interuniversity Attraction Poles project lead by the KULeuven.
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=455
Presentation given at the first annual meeting of CHARM, an Interuniversity Attraction Poles project lead by the KULeuven.
http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/repository/show?id=456
Start : 2013-05-06 - End : 2013-05-08
The 5th EISCAT_3D User Meeting is intended to focus on data
analysis and management, while on Tuesday and Wednesday pre-noon
(May 7-8) all science topics to be studied by EISCAT_3D shall be
covered.
Website:
http://www.space.irfu.se/workshops/EISCAT-3D_User2013/
Start : 2013-05-06 - End : 2013-05-10
In the last 50 years, helioseismology has made significant
contributions to the knowledge of the Sun's interior physics
and has led the way to asteroseismology. We have now reached an era
where more sophisticated questions are being asked to understand
the subtle properties of the Sun and other stars due to the
synoptic and high-resolution observations available from BISON,
GONG and space missions such as SOHO
, SDO, CoRot and Kepler.
On this occasion, a workshop on the theme of '50 years of the
seismology of the Sun and stars' is being organized to reflect the
progress that has been made as well as to focus on future goals. We
plan to bring together helio- and asteroseismologists, theorists
and observers in a journey that will take us from the interior of
the Sun and its magnetism towards the structure of distant stars
and activity cycles.
Website:
http://www.nso.edu/workshops/2013
Start : 2013-05-14 - End : 2013-05-17
Welcome to the Meeting of the Americas, a Joint Assembly that
covers topics in all areas of the geophysical sciences. Join your
colleagues, including Earth and space scientists, educators,
students, and other leaders at the Cancun Center in Cancun, Mexico,
14-17 May 2013 as they connect to present groundbreaking research.
Sandy beaches and turquoise waters together with Mexican
hospitality make this a unique site for another successful Joint
Assembly!
Session 'SH10: Solar eruptions from the photosphere to the
heliosphere' focuses on observational, modeling and theoretical
studies of coronal mass ejections (CMEs) from their formation and
initiation at the Sun to their interaction with the solar wind and
other eruptions in the interplanetary medium. We are particularly
interested in recent advancements on i) the formation or
pre-existence of flux ropes as revealed by numerical simulations
and SDO observations, ii) the rotation, expansion, deflection,
deformation and deceleration of CMEs as they propagate in the
corona and heliosphere as revealed by STEREO, IPS and radio
observations and simulations, and, iii) the understanding and
predicting of CME geo-effectiveness and how it could be improved by
future missions.
Website:
http://moa.agu.org/2013/scientific-program/sessions/sh10/
Start : 2013-05-21 - End : 2013-05-23
The sixth IAASS Conference "safety is not an option", organized
in cooperation with the International Space Safety Foundation
(ISSF), is an invitation to reflect and exchange information on a
number of topics in space safety and sustainability of national and
international interest. The conference is also a forum to promote
mutual understanding, trust, and the widest possible professional
international cooperation in such matters. The International
Association for the Advancement of Space Safety is a non-profit
organisation dedicated to furthering international cooperation and
scientific advancement in the field of space systems safety. IAASS
is a member of the International Astronautical Federation (IAF),
and Permanent Observer at the United Nations Committee on the
Peaceful Uses of Outer Space (COPUOS). The association exists to
help shape and advance an international culture of space safety
(technical, organisational and socio-political) which would
contribute to make space missions, vehicles, stations,
extraterrestrial habitats, equipment and payload safer for the
general public, ground personnel, crews and flight participants.
The association also pursues the safeguarding of the on-orbit
environment to allow unimpeded access to space by future
generations.
Website:
http://iaassconference2013.spacesafetyfoundation.org/
Start : 2013-05-22 - End : 2013-05-24
The SPENVIS User Workshop will be held at the Royal Library of
Belgium, Belgium's national and scientific library. It is one
of the most important libraries in Europe since its history goes
back to the 15th century. It is located in the heart of Brussels at
walking distance from the Central Railway Station.
The main objective of this event is to bring the SPENVIS users
together to share their experience and to identify their
requirements. The workshop will focus on the current and the
forthcoming Next Generation SPENVIS systems.
Topics include:
* Current and future SPENVIS overview
* Space Radiation Models and their accuracy
* Space Environment Effects (charging, SEE, degradation,
micro-particle impacts)
* Geant4 Tools
* Educational use of SPENVIS
* SPENVIS and other tools
Website:
http://www.spenvis.oma.be/workshop/2013/
Start : 2013-05-29 - End : 2013-06-07
Website:
http://swssuah2013.pbworks.com/w/page/60509553/FrontPage
Start : 2013-06-04 - End : 2013-06-07
Our goal is somewhat different from more familiar conferences
and is designed with the SHINE model in mind. We are inviting very
few speakers who we are asking to give review and introductory
talks for each topic we hope to discuss. Those invited review talks
will be largely non-controversial and focus upon agreed-upon
results. They are also likely to contain challenges for the
participants to explain. Then, the bulk of the time is left
unscheduled and we ask the participants to give short, focused
talks that lead to discussion and debate on the fundamental aspects
of the subject at hand.
We expect that everyone who attends will have ample opportunity
to enter into the debate and we hope to stimulate a lively
discussion of fundamental physics.
We hope you will join us. Bring multiple 5-minute talks that
attempt to make specific points so you can enter into the debate
clearly and propel the discussion forward. No one is expected to be
given a large block of time to speak. The goal is meaningful and
focused debate. Remember, you may not convince everyone, but there
will be many participants who want to understand your point of
view. Our goal is to debate and illuminate, providing inspiration
to all.
Website:
http://www-ssg.sr.unh.edu/mag/Kennebunkport2013/Kennebunkport2013.html
Start : 2013-06-15 - End : 2013-06-19
Space Climate is an interdisciplinary science that deals with
the long-term change in the Sun, and its effects in the heliosphere
and in the near-Earth environment, including the atmosphere and
climate. A special focus will be on studies of the causes,
consequences and implications of the present, unusually low solar
activity since solar cycle 23 that, most likely, indicates the
imminent end of the Modern Grand Maximum of solar activity. Other
topics include solar dynamo, solar irradiance variations, solar
wind, geomagnetic field and activity, cosmic rays and cosmogenic
isotopes, and solar effects on different layers of the atmosphere
and on local and global climate, as well as possible solar effects
on human health and on the development of human cultures.
Website:
http://www.spaceclimate.fi/
Start : 2013-06-17 - End : 2013-06-20
The workshop is to improve the scientific understanding of the
origin and propagation of solar transients, and develop the
prediction capacity of these transients' arrival and potential
impact on the Earth.
This workshop is the activity of the ISEST program in CAWSES-II
/ Task Group 3. The workshop engages coordinated international
activities in observation, theory and modeling, and involves
scientists in both developed and developing countries, and provides
an online platform for educational opportunities for students.
Website:
http://spaceweather.gmu.edu/meetings/ISEST/Home.html
Start : 2013-06-19 - End : 2013-06-19
The SWWT is a forum open to European experts in a variety of
both scientific and application oriented fields relating to space
weather. The SWWT plays an important role in advising ESA in space
weather strategy and acts as a forum for discussion amongst the
European space weather community. The SWWT is responsible for
promoting coordinated European space weather activities at both
national and industry levels. The SWWT seeks to identify and
discuss potential collaborations and/or synergies with other
structures or organisations such as the EC FP7 & COST
programmes and others.
Each year they organise a Plenary Meeting.
Start : 2013-06-20 - End : 2013-06-20
This conference aims at presenting the status of atomic physics,
plasma spectroscopy, and solar physics from space, put in the
perspective of the achievements made with SOHO and the missions
that followed.
In addition, our friend and colleague Alan Gabriel will
celebrate his 80th birthday. In anticipation of this, it will be an
excellent opportunity to celebrate his many (and continuing)
contributions to science in various fields. They range from atomic
physics and plasma spectroscopy (theta-pinch machine) to solar and
space physics - from Skylab, SMM (PI of XRP), Spacelab2, to SOHO
(GOLF, CDS, EIT, SUMER ) - as well as science management, including
RAL (UK), IAS (France), ESA SSWG (and SSAC), NASA/ESA Solar
Orbiter/Sentinels.
Presentations addressing new results in atomic physics, plasma
spectroscopy and solar physics are welcome, along with
reminiscences related to Alan, which are warmly encouraged.
Website:
http://www.ias.u-psud.fr/AHG/
Start : 2013-06-23 - End : 2013-06-29
The 2013 ILWS Science Workshop will take place June 23-29, 2013
in Irkutsk, Russia and will be hosted by the Institute of
Solar-Terrestrial Physics of the Russian Academy of Sciences
Website:
http://en.iszf.irk.ru/ILWS_2013
Start : 2013-06-24 - End : 2013-06-28
Asia Oceania Geosciences Society (AOGS) was established in 2003
to promote geosciences and its application for the benefit of
humanity, specifically in Asia and Oceania and with an overarching
approach to global issues.
Asia- Oceania region is particularly vulnerable to natural
hazards, accounting for almost 80% human lives lost globally. AOGS
is deeply involved in addressing hazard related issues through
improving our understanding of the genesis of hazards through
scientific, social and technical approaches.
AOGS holds annual conventions providing a unique opportunity of
exchanging scientific knowledge and discussion to address important
geo-scientific issues among academia, research institution and
public.
Recognizing the need of global collaboration, AOGS has developed
good co-operation with other international geo-science societies
and unions such as the European Geosciences Union (EGU), American
Geophysical Union (AGU), International Union of Geodesy and
Geophysics (IUGG), Japan Geo-science Union (JpGU), and Science
Council of Asia (SCA).
Website:
http://www.asiaoceania.org/aogs2013/public.asp?page=home.htm
Start : 2013-06-30 - End : 2013-07-04
The 2013 Radiation Belts Workshop is the first of a series of
radiation belt meetings that are planned to be held in the Aegean
islands.
As its title conveys, this first workshop includes sessions on
radiation belt research and specification. The workshop focuses, in
particular, on the properties of low frequency electromagnetic
waves and their effects on radiation belts dynamics. The other
highlight of the workshop is the ongoing international effort on
improvement of the AE9/AP9 Next Generation Radiation Specification
Models. These sessions will be complemented with presentations of
the progress achieved by a most relevant FP7-Space project titled
MAARBLE (Monitoring, Analyzing and Assessing Radiation Belt Loss
and Energization).
Website:
http://www.space.noa.gr/rbw13/
Start : 2013-07-08 - End : 2013-07-09
The goal of the symposium is to present and discuss new results
on solar activity and its manifestations in the entire heliosphere,
including geospace and other planetary environments. The new
space-borne solar observatories (SDO, Hinode, STEREO) have recently
made important new discoveries on the dynamics of the magnetized
solar atmosphere and solar wind, and on solar eruptive events that
are the main driver of variable conditions in geospace and other
planetary environments.
We now also better understand the changes of long-term solar
activity, from the low levels of 100 years ago to the all-time
maximum in the late 1950s, and to the very weak activity of the
recent minimum. Although solar and geomagnetic activity during the
ongoing cycle 24 has remained abnormally low, the increasing
activity after the long solar quiescence has recovered the
attention to space weather.
We solicit presentations covering the entire domain from the
solar surface (and below) to the heliopause, covering all time
scales of variations from a fraction of a second to millenia. The
practical aspects of solar-driven variability in space environments
(space weather) and the long-term changes in the solar activity and
its effects in the heliosphere (space climate) will be covered as
well.
Website:
http://theory.physics.helsinki.fi/~ravainio/ewass-13/
Start : 2013-07-12 - End : 2013-07-19
Applications are invited for the 2013 Heliophysics Summer
School, which will be held in beautiful Boulder, Colorado. We are
seeking students and undergraduate level teachers and instructors
to join us this coming summer for a unique professional experience.
Students and teachers will learn about the exciting science of
heliophysics as a broad, coherent discipline that reaches in space
from the Earth's troposphere to the depths of the Sun, and in
time from the formation of the solar system to the distant future.
At the same time, a goal of the Summer School is for the group of
instructors to develop materials from Heliophysics that can be
applied in their classes.
The Heliophysics Summer School focuses on the physics of space
weather events that start at the Sun and influence atmospheres,
ionospheres and magnetospheres throughout the solar system. The
solar system offers a wide variety of conditions under which the
interaction of bodies with a plasma environment can be studied:
there are planets with and without large-scale magnetic fields and
associated magnetospheres; planetary atmospheres display a variety
of thicknesses and compositions; satellites of the giant planets
reveal how interactions occur with subsonic and sub-Alfvenic flows
whereas the solar wind interacts with supersonic and super-Alfvenic
impacts.
Encompassed under a general title of comparative magnetospheres
are processes occurring on a range of scales from the solar wind
interacting with comets to the interstellar medium interacting with
the heliosphere. The school will address not only the physics of
all these various environments but will also go into the
technologies by which these various environments are being
observed. The program is complemented with considerations of the
societal impacts of space weather that affects satellites near
Earth and elsewhere in the solar system.
The school will be based on lectures, laboratories, and
recitations from world experts, and will draw material from the
three textbooks Heliophysics I-III, published by Cambridge
University Press.
Several teachers along with about 35 students will be selected
through a competitive process organized by the UCAR Visiting
Scientist Programs. The school lasts for eight days, and each
participant receives full travel support for airline tickets,
lodging and per diem costs.
Website:
http://www.vsp.ucar.edu/Heliophysics/
Start : 2013-07-16 - End : 2013-07-25
The Summer School Alpbach enjoys 36 years of tradition in
providing in-depth teaching on different topics of space science
& technology, featuring lectures and concentrated working
sessions on mission studies in self-organised working groups. 60
young highly qualified European science and engineering students
converge annually for stimulating 10 days of work in the Austrian
Alps. 4 teams compete to design a space mission judged by a jury of
experts. Students learn how to approach the design of a satellite
mission and explore new and startling ideas supported by experts.
The Summer School 2013 will focus on Space Weather
.
The purpose of the Summer School is to foster the practical
application of knowledge derived from lectures, to develop
organisational and team-work skills and to encourage creativity.
Teams will compete to design the best project, judged by an
independent jury. The teams themselves are responsible for the
selection of the subject of the project and for the team structure
and working methods.
Website:
http://www.summerschoolalpbach.at/
Start : 2013-07-22 - End : 2013-08-02
The CISM Summer School is intended to give students a
comprehensive immersion in the subject of space weather: what it
is, what it does, and what can be done about it. Space weather is
many things: beautiful when seen through the eyes of a sun-viewing
telescope, fascinating when studied for its alien worlds of
magnetic structures and phenomena, awesome when witnessed as a
solar eruption or auroral storm, and devastating to the users of
services it disrupts. Space weather links the Sun, the Earth, and
the space in between in a branching chain of consequences. Weather
systems on the Sun can spawn interplanetary storms of colossal size
and energy that envelop the whole planet in electrical hurricanes.
Such storms attack high-tech, complex, and expensive technological
systems that provide much of the infrastructure that allows modern
society to function.
Website:
https://www2.hao.ucar.edu/docs/2013-cism-summer-school
Start : 2013-08-05 - End : 2013-08-08
The goal of this workshop is to foster collaborations between
ground and space solar projects. This workshop is expected
* to provide a forum to discuss the use of current and future
observational solar facilities, and how to optimise their
scientific returns;
* to identify the potentially paradigm-shifting observations
that will become possible with the next generation ground- and
space-based solar telescopes and their advanced
instrumentation;
* to foster collaborations between researchers working at the
development of ground- and space-based projects and creation of
synergies between research programs at different wavelength
bands.
Website:
http://folk.uio.no/matsc/oslo-13/info.html
Start : 2013-08-05 - End : 2013-08-08
The goal of this workshop is to foster collaborations between
ground and space solar projects. This workshop is expected 1) to
provide a forum to discuss the use of current and future
observational solar facilities, and how to optimise their
scientific returns; 2) to identify the potentially
paradigm-shifting observations that will become possible with the
next generation ground- and space-based solar telescopes and their
advanced instrumentation; 3) to foster collaborations between
researchers working at the development of ground- and space-based
projects and creation of synergies between research programs at
different wavelength bands.
A workshop webpage and more information will follow shortly -
the purpose of this pre-announcement is to enable early bookings in
your calendar.
Start : 2013-08-16 - End : 2013-08-31
The Local Organising Committee and the Mexico National Committee
of IUGG have the great pleasure to welcome you to the 11th
Scientific Assembly of the International Association of
Geomagnetism and Aeronomy (IAGA) which is held in Mérida
Yucatán, Mexico from 26 to 31 August 2013 with the
motto: "Living on a Magnetic Planet". Our Magnetic Planet
Capricious (Changeable or Unpredictable) Field.
In order to increase the visibility and attractiveness of IAGA
to young researchers, to motivate them to play active role within
IAGA and to create (and enhance) their awareness of IAGA and sense
of belonging to IAGA, the first IAGA Summer School will be
organized just prior the Assembly. The summer school will provide
overview of the activities carried out within all the IAGA
divisions, with subjects from paleomagnetism and magnetic
anisotropy through observatories and geomagnetic field modeling to
ionospheric and aeronomic research. At least 20 young scientists
from all around the world will be invited based on the nominations
from Working Groups and Divisions. Special call and more
information will be published before the end of 2012.
Website: http://iaga2013.org.mx/
Start : 2013-08-25 - End : 2013-08-29
This conference will focus on instrumentation, observatories,
space missions, and programs for observations from the Sun to
Earth's upper atmosphere and space environment. The aim is to bring
together diverse communities working on all elements of solar
physics and space weather instrumentation.
Studying solar phenomena and monitoring space weather requires
observations using both space- and ground-based instrumentations
covering the different regions of the Sun-Earth system, the Sun,
interplanetary medium, magnetosphere, ionosphere, and thermosphere.
Papers are solicited concerning all instrumentation-supporting
solar physics and space weather. This includes, but is not limited
to, concepts, designs, fabrication processes, calibration, data
trending, information technologies, solar data mining, instrument
modeling, and satellite lifetime prediction modeling. We are also
interested in all past, current, and future solar space missions
and satellite and ground constellations of space weather
instrumentation with a strong focus on Space Situational
Awareness.
This conference is intended to provide the solar physics
community and that of Earth's space environment with a forum for
discussing the latest updates on instrumentation, observation
techniques, and programs in their respective fields, and for
proposing innovative ideas for future Sun-Earth coordinated
observations.
Website: http://spie.org/op423
Start : 2013-09-09 - End : 2013-09-14
We gain information about the universe through analysis of the
spectra from celestial objects. However, while the intensity
spectrum represents a scalar quantity but electromagnetic radiation
occurs in the form of transverse waves, the polarized spectrum
provides us with a 4-vector, the Stokes vector. The increased
amount of information space opens new windows to the universe, in
particular for the exploration of magnetic fields. It is well
recognized that the magnetic field is a primary agent responsible
for structuring and the source of all variability on intermediate
time scales, which manifests itself in all forms of solar and
stellar activity.
It is therefore not surprising that every year there are many
scientific meetings organized with the objective of studying the
role of magnetic fields in cosmic objects. What is largely missing
in these meetings is however an in-depth investigation of the
fundamental aspects of how magnetic fields can be determined by the
means of spectro-polarimetry, our main gateway to cosmic magnetism.
The primary aim of our series of Workshops is to address these
fundamental aspects, with less emphasis on the morphological and
physical properties of cosmic magnetic fields.
Website: http://spw7.ynao.ac.cn/
Start : 2013-09-16 - End : 2013-09-20
The meeting will cover a broad range of aspects of solar
physics, space science and solar-terrestrial relations. We aim to
include every side of solar and space research, including
observations, theory, and numerical modelling. The main idea behind
the meeting is to treat the entire solar-terrestrial domain as one
system, rather than each region independently.
The topics to be covered are:
* advanced solar observations
* waves and flows in the Solar atmosphere
* structure and dynamics of solar magnetic fields
* connecting analytical theory and modern numerical simulations
to observations
* new physics in numerical modelling
* linking solar interior with heliosphere
* particle acceleration in the Sun and heliosphere
* non-linear phenomena in space plasmas
* physics of magnetosphere and ionosphere
Website:
http://swat.group.shef.ac.uk/Conferences/Ukraine_UK_2013/index.html
Start : 2013-09-16 - End : 2013-09-19
This summer school targets to introduce a generation of young
researchers (advanced master students, PhDs, and junior
postdoctoral researchers) to the diverse aspects of space weather
related research.
It will introduce theoretical approaches to space weather and
its drivers, present modern solar data analysis tools, and cover
state-of-the-art solar and space science simulations. Participants
will learn about forecasting aspects and their quality control for
space weather events, but also experience hands-on training in
scientific proposal writing and receive do-and-don't tips for
scientific presentations.
The scientific program is enriched by a public evening lecture
on the solar influence on our climate, and the lecturers are
invariably expert scientists with international standing.
The school is open to a maximum of 40 participants, and can
benefit from its embedding within two international research
network activities: an Interuniversity Attraction Pole P7/08 CHARM
connecting heliospheric to astrophysical communities with 7 partner
institutes, and a European FP7 Project eHeroes with 15 different
partner institutes. Participation from outside both network
activities is strongly encouraged. Within Belgium, the school links
up expertise from universities (KU Leuven, ULB, Gent University) to
federal research institutes (the Solar-Terrestrial Centre of
Excellence, the Royal Observatory of Belgium and the Belgian
Institute for Space Aeronomy).
Website:
http://stce.be/SpSTraining/
Start : 2013-10-24 - End : 2013-10-26
Initiated by Profs. Fang and Choudhury, the first Asian-Pacific
Solar Physics Meeting (APSPM) was held in Bangalore two years ago.
During the meeting, a consensus was achieved that it might be a
good idea to have the APSPM every three years. Somehow the second
APSPM was proposed to be held by mainland China in 2013. APSPM is
aimed to exchange the recent research results in solar physics in
the emerging asian-pacific region.
Asian-pacific regions are getting more and more active in solar
physics, as signified by the construction of big facilities,
including the Hinode satellite (Japan), SOXS (India), Chinese Solar
Radio Heliogragh, and Optical & Near-Infrared Solar Eruption
Tracer (ONSET). Therefore, colleagues have agreed to hold regional
solar physics meetings regularly. The first Asian-Pacific Solar
Physics Meeting (APSPM) was held in Bangalore during March 22-24
2011. During the meeting, a consensus was achieved that it might be
a good idea to have the APSPM every three years. Somehow the second
APSPM was proposed to be held by mainland China in 2013. APSPM is
aimed to exchange the recent research results in solar physics in
the emerging asian-pacific region.
Website:
http://sdac.nju.edu.cn/~solar/
Start : 2013-10-27 - End : 2013-10-31
Magnetic helicity has been intensively studied from
observational, theoretical, and many other aspects of solar
physics. For this meeting we would like to invite solar physicists
who are interested in the observational and theoretical studies of
the helicity, to encourage thorough discussions on the relevant hot
issues. The 1st Helicity Thinkshop was held successfully in 2009,
and now the 2nd one will be held on October 27-31, 2013 in Beijing,
China.
Website:
http://sun.bao.ac.cn/meetings/HT2013/
Start : 2013-11-11 - End : 2013-11-22
Magnetic fields play an important role in many astrophysical
processes. But magnetic are difficult to detect and to model or
understand, since the fundamental equations describing the behavior
of magnetized plasmas are highly non-linear. Hence, magnetic fields
are often an inconvenient subject which is overlooked or simply
neglected. Such difficulty burdens the research on magnetic fields,
which has evolved to become a very technical subject, with many
small disconnected communities studying specific aspects and
details.
The school tries to amend the situation by providing a unifying
view of the subject. The students would have a chance to understand
the behavior of magnetic fields in all astrophysical contexts, from
cosmology to the Sun. From star-bursting regions to AGNs in
galaxies. The school will present a balanced yet complete review of
our knowledge. Extensions into the unknown are also important to
indicate present and future lines of research.
The Winter School will bring together in a relaxed working
atmosphere a number of the leading scientists in this field, PhD
students and recent postdocs. The conditions for a successful
interaction will be granted, including two special sessions for
those students that want to present their own work.
Website:
http://www.iac.es/winterschool/2013/
Start : 2013-11-12 - End : 2013-11-15
Since its launch in Sep-2006, more than 600 refereed papers have
been published based on Hinode observations, presenting many new
and important findings to the scientific community. However, due to
the unexpectedly low levels of solar activity, until now the focus
has mainly been on the more quiescent aspects of the solar cycle.
With the solar maximum expected this year, through cooperative
observations with SDO, IRIS, and ground based observatories, Hinode
observations should lead to our understanding of active Sun
phenomena, such as solar flares and CMEs, to be greatly improved.
Making Hinode-7 an excellent opportunity to discuss solar activity
in the current solar cycle and the related science through the use
Hinode data, as well as other solar/space weather data. It will
also be interesting to use this meeting to broaden our focus to
include the solar-stellar connection as a means to deepen our
understanding of solar activity.
Momentum is also gaining for Solar-C, which is being developed
as an international collaboration between Japan, US and Europe. To
further discuss this mission, the Solar-C science meeting will be
held on 11-Nov.
Website:
http://www.kwasan.kyoto-u.ac.jp/hinode-7/
Start : 2013-11-18 - End : 2013-11-22
This International CAWSES-II Symposium hosted by SCOSTEP
(Scientific Committee on Solar-Terrestrial Physics) will provide an
excellent opportunity to discuss the scientific accomplishments of
CAWSES-II and look forward to SCOSTEP's future programs at a moment
toward the end of its five-year period. The symposium will cover
the six major themes of CAWSES-II tasks: 1) What are the solar
influences on the Earth's climate?, 2) How will geospace respond to
an altered climate?, 3) How does short-term solar variability
affect the geospace environment?, 4) What is the geospace response
to variable inputs from the lower atmosphere?, 5) Capacity
Building, 6) Informatics and eScience. The main functions of
CAWSES-II are to help coordinate international activities in
observations, modeling, and applications crucial to achieving this
understanding, to involve scientists in both developed and
developing countries, and to provide educational opportunities for
students of all levels. The symposium offers keynotes/lectures that
will be interesting for all participants every morning and more
specific sessions of presentations in the afternoon. We welcome all
those who are involved and/or interested in CAWSES-II to Nagoya in
the autumn when we will have the pleasure of being surrounded by
beautiful colorful leaves of this season.
Website:
http://www.cawses.org/CAWSES/leaflet_CAWSES-II_120229.pdf
Start : 2013-11-18 - End : 2013-11-22
The 10th Edition of the European Space Weather
Week will take place on 18-22nd
November 2013 in Belgium. The venue will be confirmed early next
year, but mark your calendars now for the 10th Anniversary of this
growing European event.
The ESWW will again adopt the central aim of bringing together
the diverse groups in Europe working on different aspects of Space
Weather
. This includes but isn't
limited to the scientific community, the engineering community,
applications developers, service providers and service end users.
The meeting organisation will again be coordinated by the Belgian
Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE), ESA
and the Space Weather
Working Team. The local
organisation will be done by the STCE.
Website:
http://www.stce.be/esww10/
Start : 2014-08-02 - End : 2014-08-10
The 40th COSPAR Scientific Assembly will be held in Moscow,
Russia from 2 - 10 August 2014. This Assembly is open to all bona
fide scientists.
Website:
http://www.cospar-assembly.org/