- Table of Content
- 1.PROBA2 Observa...
- 2.Review of sola...
- 3.SIDC Space Wea...
- 4.The Internatio...
- 5.Geomagnetic Ob...
- 6.Review of iono...
- 7.Future Events
2. Review of solar and geomagnetic activity
3. SIDC Space Weather Briefing
4. The International Sunspot Number
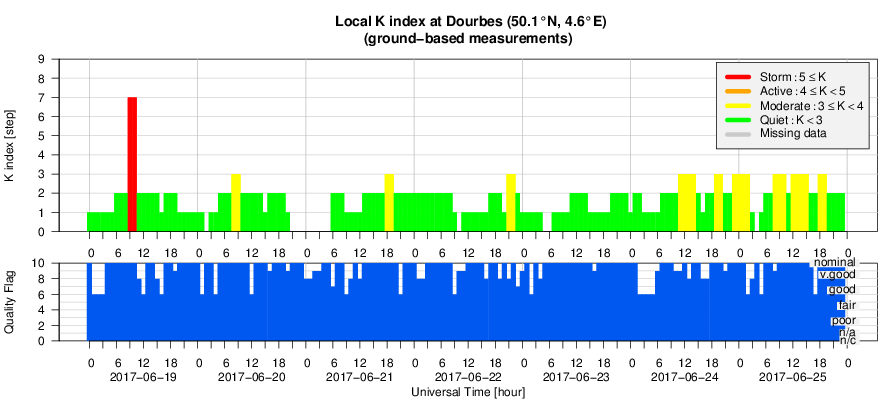
5. Geomagnetic Observations at Dourbes (19 Jun 2017 - 25 Jun 2017)
6. Review of ionospheric activity (19 Jun 2017 - 25 Jun 2017)
7. Future Events
PROBA2 Observations (19 Jun 2017 - 25 Jun 2017)
Solar Activity
Solar flare activity remained very low during the week.
In order to view the activity of this week in more detail, we suggest to go to the following website from which all the daily (normal and difference) movies can be accessed: http://proba2.oma.be/ssa
This page also lists the recorded flaring events.
A weekly overview movie can be found here (SWAP week 378):
http://proba2.oma.be/swap/data/mpg/movies/weekly_movies/weekly_movie_2017_06_19.mp4
Details about some of this week's events, can be found further below.
If any of the linked movies are unavailable they can be found in the P2SC movie repository here:
http://proba2.oma.be/swap/data/mpg/movies/
Monday Jun 19
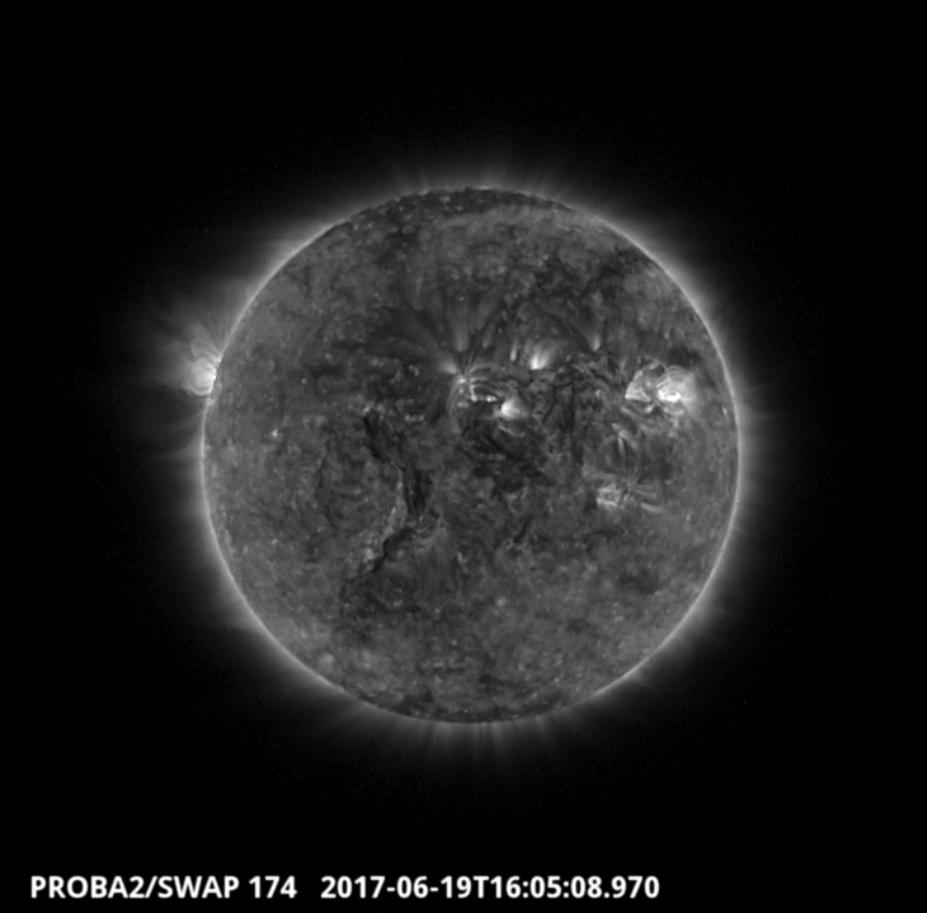

The largest flare of the week (B5.0) was from NOAA active region 2663 and occurred on 2017-Jun-19 in the north-eastern quadrant of the Sun, as shown in the SWAP image above at 16:05 UT.
Find a movie of the event here (SWAP movie):
http://proba2.oma.be/swap/data/mpg/movies/20170619_swap_movie.mp4
Review of solar and geomagnetic activity
SOLAR ACTIVITY
Over the past week solar activity has been low. No significant flares were recorded. The largest was a B5.0 flare from Active Region (AR) 2663. AR 2663 was most active throughout the week, producing several B-class flares, however the region moved over the west solar limb on 21 Jun 2017. No Earth directed Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs) were detected. AR 2664 emerged over the east solar limb on 20 Jun 2017 and produced a couple of small eruptions. A small northern coronal hole transited the solar disk throughout the week, the region extended toward lower latitudes, but only increased the solar wind speed at Earth marginally. The greater than 10 MeVproton flux remained at background levels.
GEOMAGNETIC ACTIVITY
Over the past week the solar wind speed fluctuated between 330 and 530 km/s. At the beginning of the week the solar wind speed was in decline before starting to slowly increase again around 23 Jun 2017. The total magnetic field strength has fluctuated between 4 and 10 nT. The Bz component fluctuated between -6 and +7 nT. During this week geomagnetic conditions were mostly quiet to unsettled, where the Kp-index ranged between 0 and 4 (NOAA) and local K-index between 0 and 3 (Dourbes).
SIDC Space Weather Briefing
The Space Weather Briefing presented by the forecaster on duty from June 19 to 25 2017. It reflects in images and graphs what is written in the Solar and Geomagnetic Activity report.

The powerpoint: http://www.stce.be/newsletter/SWBriefings/SWbriefing_20170626.pptx
The International Sunspot Number
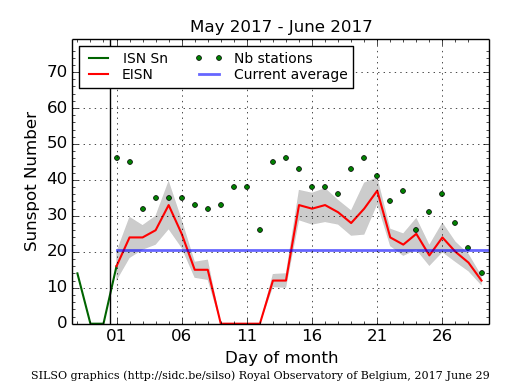
The daily Estimated International Sunspot Number (EISN, red curve with shaded error) derived by a simplified method from real-time data from the worldwide SILSO network. It extends the official Sunspot Number from the full processing of the preceding month (green line). The plot shows the last 30 days (about one solar rotation). The horizontal blue line shows the current monthly average, while the green dots give the number of stations included in the calculation of the EISN for each day.
Review of ionospheric activity (19 Jun 2017 - 25 Jun 2017)
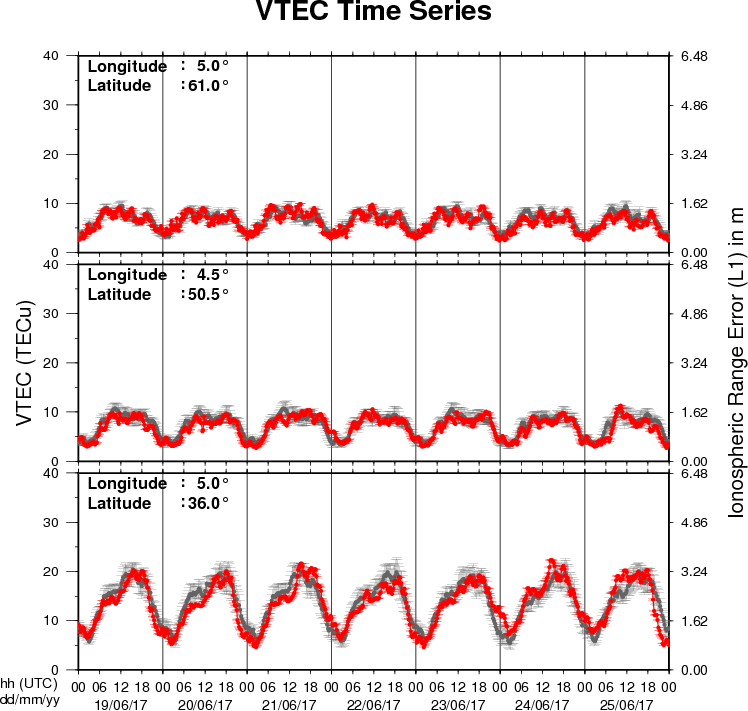
The figure shows the time evolution of the Vertical Total Electron Content (VTEC) (in red) during the last week at three locations:
a) in the northern part of Europe(N61°, 5°E)
b) above Brussels(N50.5°, 4.5°E)
c) in the southern part of Europe(N36°, 5°E)
This figure also shows (in grey) the normal ionospheric behaviour expected based on the median VTEC from the 15 previous days.
The VTEC is expressed in TECu (with TECu=10^16 electrons per square meter) and is directly related to the signal propagation delay due to the ionosphere (in figure: delay on GPS L1 frequency).
The Sun's radiation ionizes the Earth's upper atmosphere, the ionosphere, located from about 60km to 1000km above the Earth's surface.The ionization process in the ionosphere produces ions and free electrons. These electrons perturb the propagation of the GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) signals by inducing a so-called ionospheric delay.
See http://stce.be/newsletter/GNSS_final.pdf for some more explanations ; for detailed information, see http://gnss.be/ionosphere_tutorial.php
Future Events
For more details, see http://www.spaceweather.eu/en/event/future
United Nations/United States of America Workshop on the International Space Weather Initiative in Massachusetts (USA)
Start : 2017-07-31 - End : 2017-08-04
This workshop marks the 10th anniversary of the International
Heliophysical Year, which led to the genesis of the International
Space Weather Initiative. It is organized jointly by the Office for
Outer Space Affairs, the National Aeronautics and Space
Administration (NASA) and Boston College to highlight the
achievements made over the past ten years and to show-case the
worldwide development of science, capacity building, and
outreach.
The UN Workshops on ISWI have been aimed at providing a global
forum for space weather experts from developed and developing
countries, including representatives of the major instrument
operators and data providers. In particular the Workshop will focus
on recent advances made in scientific research by utilizing ISWI
instrument data in conjunction with space mission data in adding
significant new knowledge on space weather phenomena near Earth and
interplanetary space.
The workshop will begin with a high level international forum on
the economic and societal effects of extreme space weather. This
forum will include keynote speakers from major international
organizations followed by a panel session to discuss issues and
policies for acknowledging space weather as a global challenge.
The workshop is also held in preparation for UNISPACE+50 in
2018, the 50th anniversary of the first UN Conference on the
Exploration and Peaceful Uses of Outer Space (UNISPACE), held in
Vienna in 1968. The three components of the Workshop will also help
develop a coherent international policy towards an appropriate
response to space weather.
Website: https://iswi2017.bc.edu/
URSI General Assembly in Montreal, Canada
Start : 2017-08-19 - End : 2017-08-26
For the thirty-second time since the inception of URSI, Radio
Scientists from across the world will get together for the URSI
General Assembly and Scientific Symposium. This triennial gathering
will take place from 19th to 26th of August 2017, in Montreal,
Canada. This conference is a unique opportunity to learn about
recent advances in all fields of Radio Science, as covered by all
ten URSI Commissions.
Among the different sessions, please note:
* 'Radio Science for Space Weather'
Conveners: M. Messerotti, V. Pierrard
* 'Remote Sensing and Modeling of the Earth's Plasmasphere
and Plasmapause'
Conveners: A. M. Jorgensen, V. Pierrard, B. Heilig
The abstract deadline is 30 January 2017
Website: http://www.ursi2017.org
2017 Joint IAPSO-IAMAS-IAGA Assembly in Cape Town, South Africa
Start : 2017-08-27 - End : 2017-09-01
The Joint IAPSO-IAMAS-IAGA Assembly, endorsed by the University
of Cape Town and the South African Department of Science and
Technology, will take place from 27 August to 1 September 2017 at
the Cape Town International Convention Centre (CTICC). Several IAGA
and IAMAS sessions are of Space Weather interests as well as the
joint session 'Space Weather throughout the Solar System: Bringing
Data and Models together'.
Website:
http://iapso-iamas-iaga2017.com/index.php
Workshops on Radiation Monitoring for the International Space Station in Torino, Italy
Start : 2017-09-05 - End : 2017-09-07
The Workshop on Radiation Monitoring for the International Space
Station is an annual meeting to discuss the scientific definition
of an adequate radiation monitoring package and its use by the
scientific community on the ISS. Types of instruments and research
topics need to be defined in order to optimise the radiation safety
of the ISS crew.
Website: http://wrmiss.org/
International Workshop on Solar, Heliospheric & Magnetospheric Radioastronomy in Meudon, France
Start : 2017-11-06 - End : 2017-11-10
Jean-Louis Steinbeg has been one of the major pioneers in
radioastronomy. Co-founder of the Nançay Observatory, he
has actively participated to, an inspired a large number of radio
instruments on many international space missions. Jean-Louis
Steinberg is the founder of the Space Radioastronomy laboratory of
the Paris Observatory in 1963. Later on, this laboratory widened
its science interests and became the DESPA (1971) and then the
current LESIA (2002) which is one of the major space sciences
laboratories in France. The aim of this workshop is to cover the
science topics which Jean-Louis Steinberg has promoted during his
career, focusing on Solar, Heliospheric & Magnetospheric
radioastronomy & physics. This will be done by covering both
observations from either ground facilities (NDA, RH, LOFAR, Artemis
etc ...) or space missions (ISSEE, Ulysses, WIND, CLUSTER, STEREO,
CASSINI, JUNO etc ...) and models/theories. A series of invited
talks is also foreseen to cover the new developments in the
discipline which may come with the future facilities such as Solar
Orbiter, Solar Probe Plus, JUICE, JUNO, LOFAR+, SKA etc ....
This workshop will also be the opportunity to remember both the
extraordinary personal & professional lifes of Jean-Louis
Steinberg especially for new generation of scientists. At the
occasion of this workshop it is also expected that the Building 16
(historical Space Sciences building) on the Meudon campus will be
renamed "Building Jean-Louis Steinberg".
Website:
https://jlsworkshop.sciencesconf.org/
European Space Weather Week 14
Start : 2017-11-27 - End : 2017-12-01
The ESWW is the main annual event in the European Space Weather
calendar. It is the European forum for Space Weather as proven by
the high attendance to the past editions. The agenda will be
composed of plenary/parallel sessions, working meetings and
dedicated events for service end-users. The ESWW will again adopt
the central aim of bringing together the diverse groups in Europe
working on different aspects of Space Weather.
Website:
http://www.stce.be/esww14/