news
Submitted on 2016-05-19We are still far from the year's end, yet we already received an application for the most impressive solar event of the year. A relatively modest C3 flare ...
Submitted on 2016-05-05X-class flares are "eXtreme" x-ray solar events, 10 times more powerful than a "medium" M-class flare, and 100 times more powerful than the "common" C-class flares.
Submitted on 2016-04-26The big sunspot group NOAA 2529 was a relatively quiet region before producing an M6 flare early on 18 April. The coronal mass ejection (CME) associated with this "medium" flare was not directed to Earth.
Submitted on 2016-04-19Over the last two weeks, the Sun's outlook has been dominated by the big active region NOAA 2529. This sunspot group was relatively quiet, producing only a handful of low-level C-class flares... before erupting in a strong M6 flare early on 18 April. Despite being quiet most of the time, close examination of the available imagery showed important dynamics in the region, in particular the main spot. Note that at its maximum size, the main spot had a diameter of almost 5 times that of the Earth, and its total surface area was over 5 times that of our planet.
Submitted on 2016-04-12
Solar activity has been very low over the last weeks, with very few or no C-class flares at all. The x-ray background flux was also low, at or just below the B1 level. Around noon on 5 April, this background flux started a gentle increase to values slightly above B3 on 7 April, coinciding with the appearance of a big sunspot near the solar east limb.
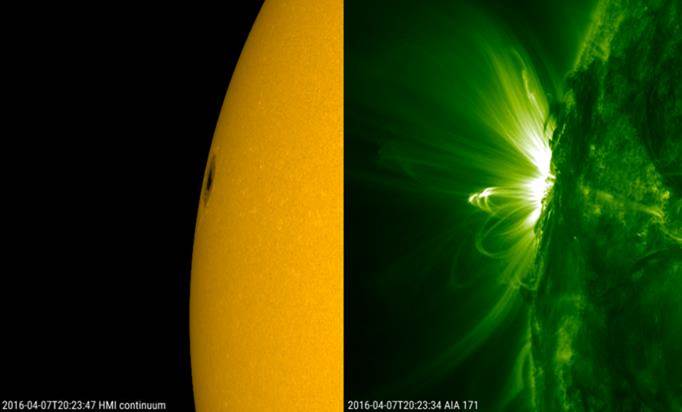

Submitted on 2016-04-05
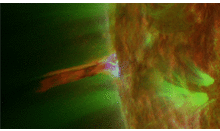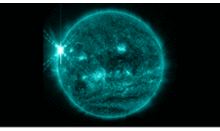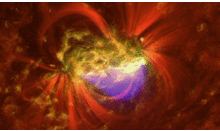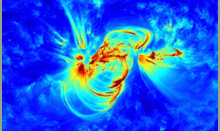
Solar prominences are clouds of charged particles ("plasma") above the solar surface squeezed between magnetic regions of opposite polarity. Being cooler and denser than the plasma underneath and their surroundings, they appear as bright blobs when seen near the solar limb and as dark lines when seen on the solar disk (then they are called "filaments"). Special filters are required to observe these features, such as in the Hydrogen-alpha (H-alpha) line in the red part of the solar spectrum, or in some extreme ultraviolet (EUV) passbands.
Submitted on 2016-03-31
Continuing the ongoing trend of low solar activity, last week was once again very quiet with flaring levels barely reaching the C-class level. Only NOAA 2524 was able to produce a C1 flare on 23 March (long duration event), and a C2 flare early on Monday 28 March. By then, this active region had decayed into a small single sunspot and was rounding the west limb. Despite its simple outlook, this region showed quite some activity in extreme ultraviolet wavelengths.

Submitted on 2016-03-10
On 2016 March 8 and 9, a solar eclipse took place over the Pacific Ocean. This eclipse was total - that is, the entire solar disk was covered by the Moon- over Indonesia and the central Pacific, starting at sunrise over Sumatra and ending at sunset north of the Hawaiian Islands. Additionally, large parts of South-East Asia, Alaska and Australia witnessed a partial solar eclipse. The path of totality had a maximum width of 155 km and the maximum duration was 4 minutes and 9 seconds at the point of greatest eclipse, which was over the waters of the Pacific Ocean.
Submitted on 2016-02-24When observing the Sun for a prolonged period of time, it soon becomes evident that features on its surface, and in its outer atmosphere do not rotate at the same rate. This is because the Sun is not a solid body, but a big ball of magnetised plasma, whose rotation is variable with position and height in the solar atmosphere.
Pages
Zircon - This is a contributing Drupal Theme
Design by
WeebPal.