news
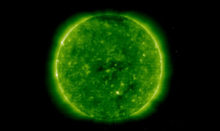
Submitted on 2009-12-14This news item was written by F. Clette from the SIDC/WDC.
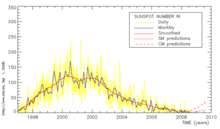
Submitted on 2009-07-31The SIDC provides the International Sunspot Number (ISN) in different forms and on different time scales: estimated, provisional, definitive, daily, monthly, monthly smoothed, yearly, ASCII, graphs. The choice is up to you.
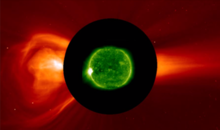
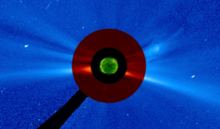
Submitted on 2009-02-10 We have the honor to welcome E. Parker in June 2009 at the Solar-Terrestrial Center of Excellence. This will be an occasion to speak to the world's top expert on the solar wind. It was in the 1950s that Parker developed his theory about the solar wind. In the perception of many, his name is a synonym for solar wind. Parker suggested that the corona, the exterior part of the solar atmosphere is continuously expanding. This spherically symmetric expansion is called the solar wind.
We have the honor to welcome E. Parker in June 2009 at the Solar-Terrestrial Center of Excellence. This will be an occasion to speak to the world's top expert on the solar wind. It was in the 1950s that Parker developed his theory about the solar wind. In the perception of many, his name is a synonym for solar wind. Parker suggested that the corona, the exterior part of the solar atmosphere is continuously expanding. This spherically symmetric expansion is called the solar wind.
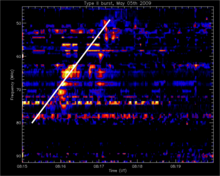
Submitted on 2008-12-31A compilation of the most memorable space weather moments of 2008 can be found underneath. Using the fantastic (J)Helioviewer software, a ***MOVIE*** was created containing one or more clips of each event. Usually, images obtained by SOHO and the STEREO spacecraft were used.
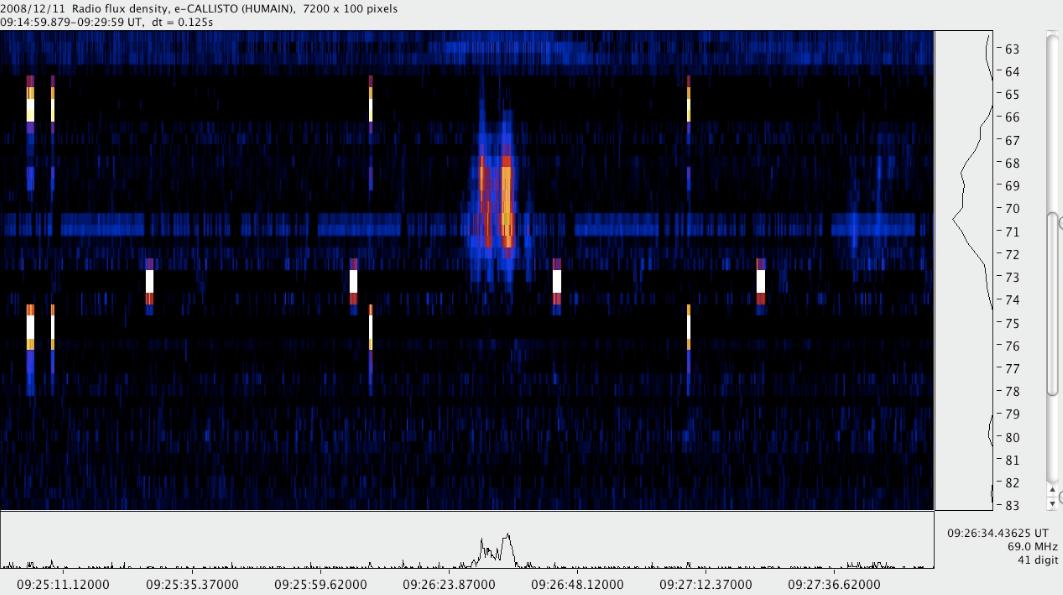
Submitted on 2008-09-18
|
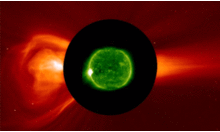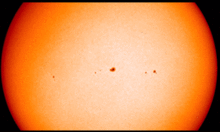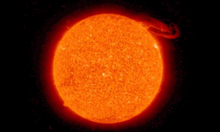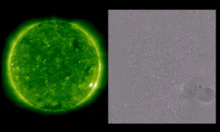
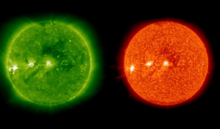
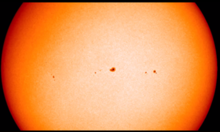
The sunspot number is the oldest index for solar activity. The International Sunspot Index is the sunspot number calculated by the World Data Center for the sunspot index. The number has different appearances depending on the extent of the used data, the date of calculation, the time period over which we take a mean, the used method. We briefly present the different daily sunspot numbers.
|
| Click on the titles to get the info behind it. |
|
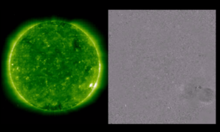
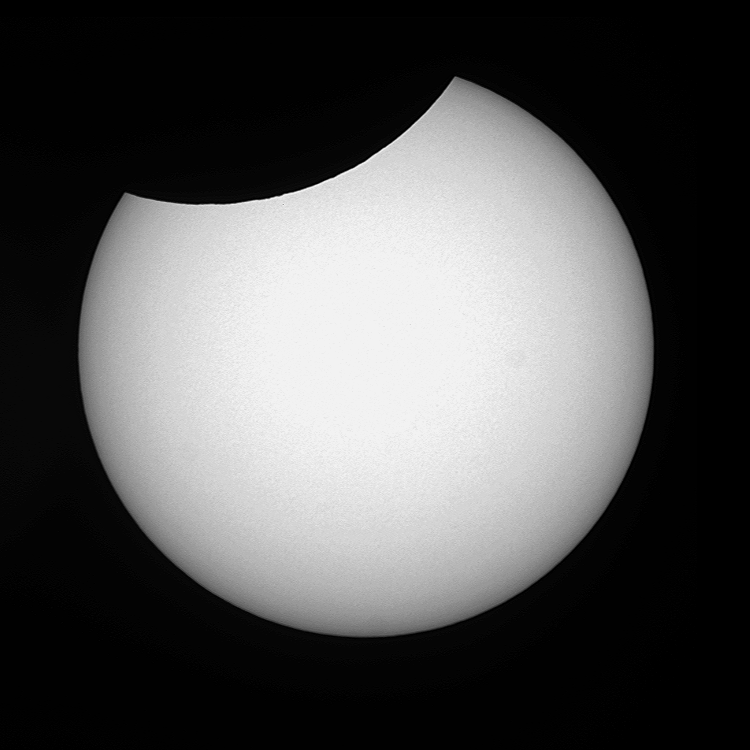
Submitted on 2008-08-01
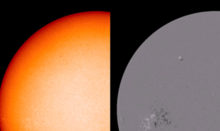
A new camera recently installed at the Uccle Solar Equatorial Table spotted the Moon in front of the Sun at 13:13. The picture was taken in normal visible (white) light, to study the photosphere of the sun. Note the complete lack of sunspots due to solar minimum.
|
 |
|
|
Pages
Zircon - This is a contributing Drupal Theme
Design by
WeebPal.



 We have the honor to welcome E. Parker in June 2009 at the Solar-Terrestrial Center of Excellence. This will be an occasion to speak to the world's top expert on the solar wind. It was in the 1950s that Parker developed his theory about the solar wind. In the perception of many, his name is a synonym for solar wind. Parker suggested that the corona, the exterior part of the solar atmosphere is continuously expanding. This spherically symmetric expansion is called the solar wind.
We have the honor to welcome E. Parker in June 2009 at the Solar-Terrestrial Center of Excellence. This will be an occasion to speak to the world's top expert on the solar wind. It was in the 1950s that Parker developed his theory about the solar wind. In the perception of many, his name is a synonym for solar wind. Parker suggested that the corona, the exterior part of the solar atmosphere is continuously expanding. This spherically symmetric expansion is called the solar wind.